Running ABM3 ¶
This page describes how to create and run an ABM3 scenario.
Creating an ABM3 Scenario ¶
Note: This section mainly relevant to SANDAG users.
Follow the steps below to create an ABM3 scenario directory:
- Check for an available server using the SANDAG Live Report: ABM Compute Servers page
- Log onto available server and ensure:
- Server’s C Drive has at least 500 GB worth of space
- You are logged onto the Bentley CONNECTION Client license manager software
- Using the server’s Windows Explorer, navigate to the latest approved ABM3 release. As of March 2025, this is T:\ABM\release\ABM\version_15_2_2
- Double click on createStudyAndScenario.bat and click Run.
- On pop-up, fill out the fields under Create an ABM scenario.
- EMME Version: As of March 2025, only available version is 4.3.7
- Year: Using drop-down menu, select scenario year you’d like to run
- Base: Whether you would like to run a Build or No Build scenario. Note that the base 2022 year only has the option to run as Base.
- Geography ID: Leave as 1. As of March 2025, this field has no functionality.
- Scenario Folder: File path you would like to create scenario at. The tool will create the directory if it doesn’t already exist. For cases where you point to an exisitng directory, the tool will notify users that location exists to avoid unintended overwriting.
- Network Folder: File path to input network.
- Land Use Folder: File path to input land use files.
- After fields are filled out, click Create.
- A DOS window will open and all required files will be copied. If you have a server with a valid license, it will pause for about 30-45 seconds on init EMME folder. You will get a pop-up window that indicates you have successfully created the scenario. Click Quit. Then, you may exit the GUI by clicking on Quit.
- Navigate to newly created scenario and ensure the correct input files were copied over.
Running ABM3 ¶
To open the EMME application from the created scenario directory, users need to go to the emme_project folder, and double-click on the start_emme_with_virtualenv.bat file. This opens up the EMME application, where the application prompts the choice of a scenario. It is recommended to select the main highway scenario (Scen. 100) to start off the model run, although other scenarios may be selected as well.
Following this step, users should open the EMME Modeler by clicking on the gold square icon at the top left of the screen.
EMME Modeler icon
The EMME Modeler opens to the EMME Standard Toolbox, but needs to be switched to the SANDAG toolbox by selecting it from the bottom-left of the screen. From this toolbox, open the Master Run tool by double-clicking it.
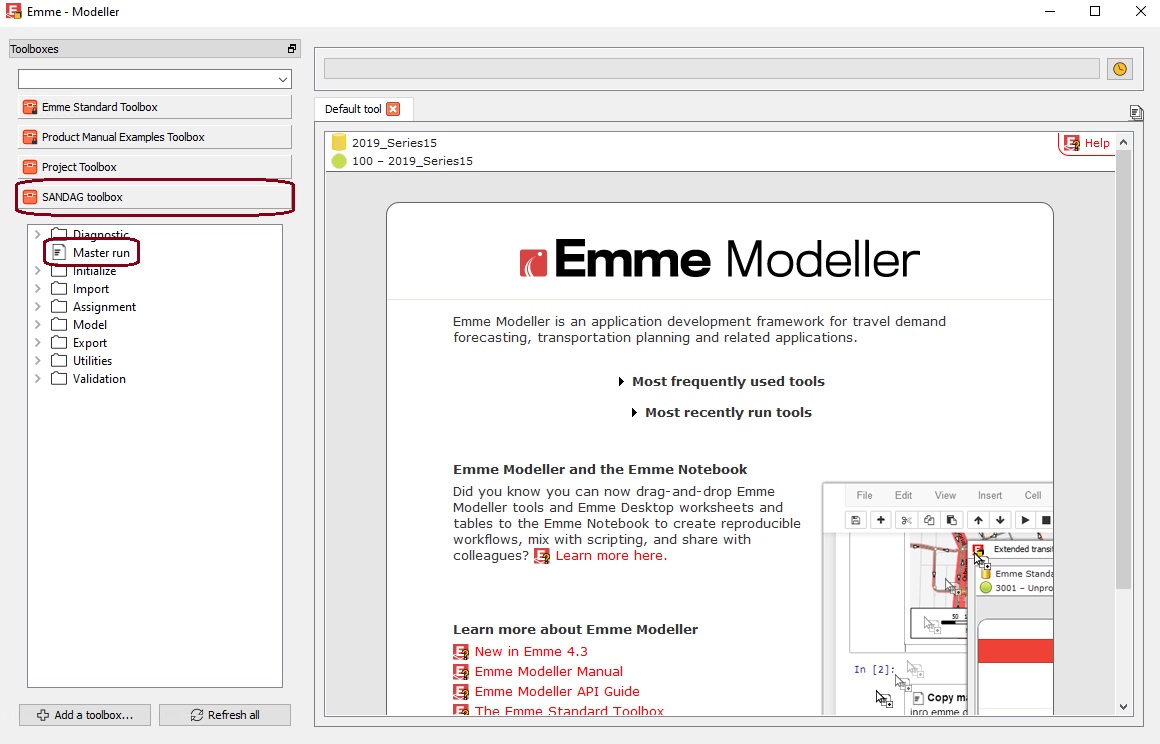
Opening SANDAG Toolbox and Master run
The Master Run tool allows the user to run all or part of the model, and set a number of settings such as sample size per iteration.
Master Run tool
The Master run tool operates the SANDAG travel demand model. Users have the option to configure a number of settings prior to launching the model run:
- Select main ABM directory: No changes necessary. The file path to the scenario. Defaults to the parent directory of opened EMME project.
- Scenario ID: No changes necessary. Scenario ID for the base imported network data. The result scenarios are indexed in the next five scenarios by time period.
- Scenario title: Title to use for the scenario. Standard practice is to input scenario title.
- Emmebank title: Title to use for the Emmebank (EMME database). Standard practice is to input scenario title.
- Number of processors: the number of processors to use for traffic and transit assignments and skims, aggregate demand models (where required) and other parallelized procedures in Emme. Default is
Max available – 1. - Datalake Environment: Datalake environment to which scenario outputs will be loaded onto: Prod (Production), or Dev (Development). This parameter mostly relevant to SANDAG users.
- Sampe rate by iteration: Three comma-separated values for the ActivitySim sample rates for each iteration.
By expanding the Run model – skip steps drop down, the user has the option to skip certain steps of the model run. Usually, the defaults (see image below) should be sufficient. It should be noted that checkmarking a step means that it will be skipped.
Run model tool
On opening the Master run tool, the conf/sandag_abm.properties file is read and its values pre-set the Run model - skip steps inputs. When the Run button is clicked, this file is written out with the values specified. Any manual changes to the file in-between opening the tool and clicking the Run button are overwritten.
- Start from iteration: Indicate from what iteration you would like model run to start.
- Skip steps: Optional checkboxes to skip model steps.
- Select link(s): Add select link analyses for traffic.
Following this setup, you can click Run to start the model run. It is recommended to occasionally check the model run status to make sure the run is going smoothly. When the model run finishes successfully, the Master run tool will show a model run successful message in green at the top of the tool window.
If the run is unsuccessful (there will be an error prompt from EMME), check the EMME Logbook and log files (under the logFiles or output directories) for clues to where it may have crashed.
As the model runs, a full runtime trace of the model steps, inputs and reports is recorded in the Modeller Logbook. As each step completes, it will record an entry in the Logbook along with reports and other results. The Logbook can be opened from the clock-like icon in the upper right of the Modeller window. This icon can also be found in the upper left toolbar in the EMME Desktop, or upper right in the EMME Logbook. If a Modeller tool is running, a window will pop-up over the EMME Desktop which includes a Show Logbook button (this window can be closed to use Desktop worksheets and tables while any tool is running). Click on the Refresh button to update the Logbook view with the latest status.
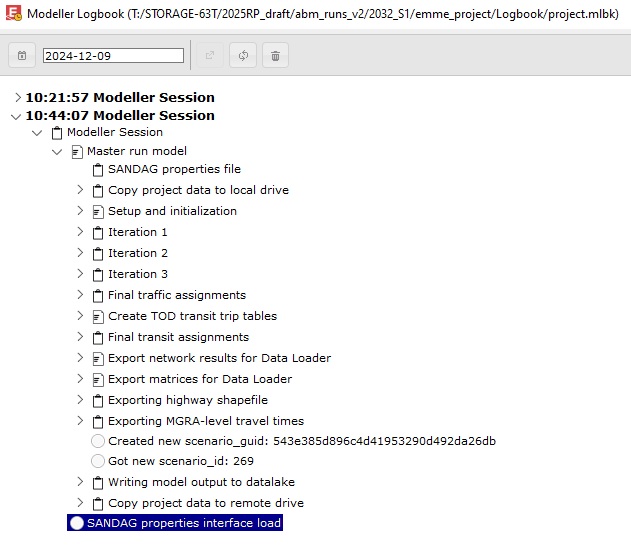
Modeller logbook
The Logbook provides a real-time, automated documentation of the model execution. The overall structure of the model is represented at the top level, with the occurrence, sequence and repetition of the steps involved in the model process. Nested Logbook entries may be collapsed or expanded to see detail. For the EMME assignment procedures, interactive charts are recorded. The statistical summaries of the impedance matrices are recorded for each time period following the assignment. These summary tables provide an easy way to check for skims with obvious outlier values.
Rerunning an ABM3 Scenario ¶
Note: This section mainly relevant to SANDAG users.
Within the SANDAG workspace, an ABM3 scenario is typically created on an internal shared drive called the T Drive. If the Use the local drive during the model run is checkmarked within the Master Run tool, when launched, the scenario is first copied over and then ran on the machine’s local Drive (i.e. C Drive). After model completion, all necessary files are copied back to the T Drive and the scenario is deleted off the C Drive.
If the same scenario from above would like to be reran:
- From beginning to end (i.e., from iteration 1):
- The modeler simply needs to open the scenario via the start_emme_with_virtualenv.bat file (on T Drive), edit (if applicable) the setup in the Master Run tool, and launch.
- Or, starting from the 2nd or 3rd iteration:
- The modeler must copy the entire ABM3 scenario to the machine’s C Drive (typically under C:\abm_runs\{username}). In particular, the modeler should ensure the files found within the emme_project folder are present on the C Drive before relaunching the scenario.
- From there, the modeler may open the scenario via the start_emme_with_virtualenv.bat file on the T Drive, edit the setup in the Master Run tool, and launch.
Note that under the above two workflows, the original scenario’s (on T Drive) outputs will be overwritten when the scenario is copied from the C Drive back to the T Drive. The modeler should consider saving the original scenario’s outputs in a different location if wanting to preserve the original data.
An alternative workflow, that may be useful for development or debugging purposes, involves rerunning the scenario entirely on the C Drive. It should be noted that under this worfklow, the model outputs of the rerun will not be copied back to the T Drive as part of the model run flow (may be copied over manually if desired). To proceed with this workflow:
- The modeler must copy the entire ABM3 scenario to the machine’s C Drive (typically under C:\abm_runs\{username}).
- Then, the modeler must open the scenario via the start_emme_with_virtualenv.bat file on the C Drive.
- Lastly, in addition to any desired setup edits under the Master Run tool, the modeler must uncheck Use the local drive during the model run so that the model run does not attempt to copy scenario files to a different drive.
One other point the modeler should consider when rerunning a scenario is whether model outputs should be loaded onto Azure Data Lake, which is controlled via the Skip write to datalake parameter under the Master Run tool:
- Unchecking this step will result in model outputs being loaded onto Azure Data Lake under a new scenario ID and will not overwrite the original run’s data on Azure Data Lake
- Checkmarking this step will skip model outputs from being loaded onto Azure Data Lake. This will likely be the preferred approach for scenario reruns related to development or debugging purposes.